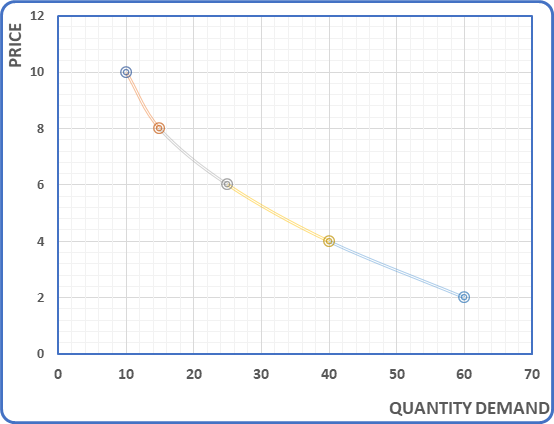
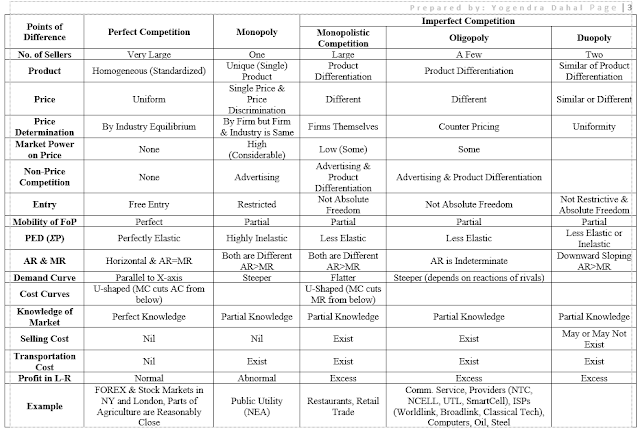
Unit 1 - Basic Concepts of Economics and Allocation of Resources (Exercise)
Write Short Notes On Subject matter of economics Goods and services Normal goods and Giffen goods Inferior goods Complementary and substitute goods with suitable example Economic goods